
The Pedi
South African Culture
Pedi was previously used to describe Sotho-speakers of Mpumalanga and Northern Province in South Africa. More recently, these groups have been renamed Northern Sotho.
Pedi initiates circle an elder.
The Pedi, as more narrowly understood, are part of the Highveld Sotho who live on the plateau around Pietersburg. Other Northern Sotho subgroups, over many of whom the Pedi once held sway, are the Lowveld Sotho along and below the Drakensberg Escarpment, and the Eastern Sotho in the Mapulaneng district, towards Lydenburg.

Subsequent to their defeat at the hands of the British, the Pedi were relegated to a series of officially designated reserves. Foremost amon...
more
Pedi culture traditionally distinguished sharply between the sexes at all levels. This affected every sphere of their lives, from the knots ...
more
By the height of their power the Pedi or Maroteng, under the leadership of Thulare (about 1790—1820), were launching frequent, successful ...
more
Like other Bantu-speaking peoples, a Pedi marriage (lenyalo) does not just legalize a relationship between individuals: it is a group concer...
more
Important Pedi crafts include pottery, house-painting, woodworking (especially making drums), metalsmithing and beadwork. Traditional music ...
more
Like the Sotho and Tswana, the Pedi, in pre-conquest times, lived in large villages divided into kgoro groups centred on family clusters fav...
more
The Pedi once held sway over most of the area flanked by the Limpopo, Vaal and Komati rivers. Their power centralized in what is today known...
more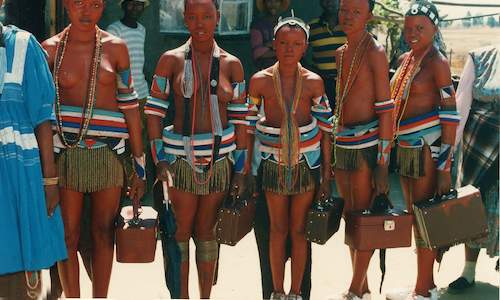
On the day the male Pedi bogwera initiation session ended, the byale (the girls' initiation) began. Only girls who had undergone a puberty c...
more
The timing of initiation, which was (and is) always in midwinter, was dependent on the presence of a high-ranking son or grandson of a chief...
more
According to oral tradition, the Pedi can be traced back to the Maroteng, an offshoot of the Kgatla, today an important component of the Tsw...
more
 Subsequent to their defeat at the hands of the British, the Pedi were relegated to a series of officially designated reserves. Foremost amon...
Subsequent to their defeat at the hands of the British, the Pedi were relegated to a series of officially designated reserves. Foremost amon... Pedi culture traditionally distinguished sharply between the sexes at all levels. This affected every sphere of their lives, from the knots ...
Pedi culture traditionally distinguished sharply between the sexes at all levels. This affected every sphere of their lives, from the knots ... By the height of their power the Pedi or Maroteng, under the leadership of Thulare (about 1790—1820), were launching frequent, successful ...
By the height of their power the Pedi or Maroteng, under the leadership of Thulare (about 1790—1820), were launching frequent, successful ... Like other Bantu-speaking peoples, a Pedi marriage (lenyalo) does not just legalize a relationship between individuals: it is a group concer...
Like other Bantu-speaking peoples, a Pedi marriage (lenyalo) does not just legalize a relationship between individuals: it is a group concer... Important Pedi crafts include pottery, house-painting, woodworking (especially making drums), metalsmithing and beadwork. Traditional music ...
Important Pedi crafts include pottery, house-painting, woodworking (especially making drums), metalsmithing and beadwork. Traditional music ... Like the Sotho and Tswana, the Pedi, in pre-conquest times, lived in large villages divided into kgoro groups centred on family clusters fav...
Like the Sotho and Tswana, the Pedi, in pre-conquest times, lived in large villages divided into kgoro groups centred on family clusters fav... The Pedi once held sway over most of the area flanked by the Limpopo, Vaal and Komati rivers. Their power centralized in what is today known...
The Pedi once held sway over most of the area flanked by the Limpopo, Vaal and Komati rivers. Their power centralized in what is today known...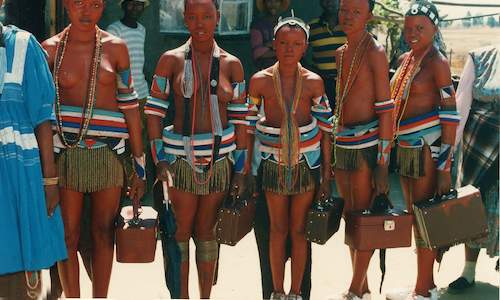 On the day the male Pedi bogwera initiation session ended, the byale (the girls' initiation) began. Only girls who had undergone a puberty c...
On the day the male Pedi bogwera initiation session ended, the byale (the girls' initiation) began. Only girls who had undergone a puberty c... The timing of initiation, which was (and is) always in midwinter, was dependent on the presence of a high-ranking son or grandson of a chief...
The timing of initiation, which was (and is) always in midwinter, was dependent on the presence of a high-ranking son or grandson of a chief... According to oral tradition, the Pedi can be traced back to the Maroteng, an offshoot of the Kgatla, today an important component of the Tsw...
According to oral tradition, the Pedi can be traced back to the Maroteng, an offshoot of the Kgatla, today an important component of the Tsw...