
Climate and Farming in South Africa
Farming is not only about choosing a crop or an animal to farm. To farm successfully and to understand nature you will need to understand the climate, weather, rainfall and temperature of an area.
Crops grow best where temperature, rainfall and climate are optimal for that specific crop.
This range of articles on climate and farming in South Africa will explain some basic natural phenomena that can influence farming and the crops we choose.
This content on climate and farming in South Africa is sourced from training material for extension advisors developed by a team of consultants lead by the University of Pretoria. Researchers include Dr Joe Stevens, Pieter van Heerden and Prof MC Laker. The project was funded by the Water Research Commission (WRC).
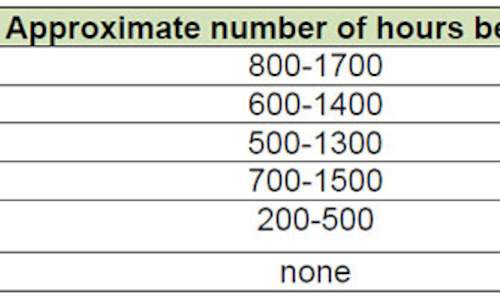
A plant needs periods of heat and cold for certain processes in its growth cycle. These periods of heat and cold are expressed in heat units...
more
In farming areas where frost can damage crops, good management of planting times can limit frost damage during the growth period of crops....
more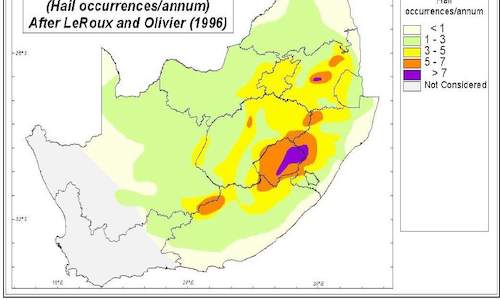
Similar to rain, hail is a form of precipitation and can contribute to the availability of water in a farming area, but can also cause exten...
more
Most of South Africa is a summer rainfall area, November to March, while the Western Cape Province receives most of its rain during winter, ...
more
Snow, mist and dew are forms of precipitation that contribute to the available moisture in a farming area. Mist is common along the cool are...
more
South Africa falls in a temperate zone, south of the equator, with summers from November to March and winters from May to August. Its temper...
more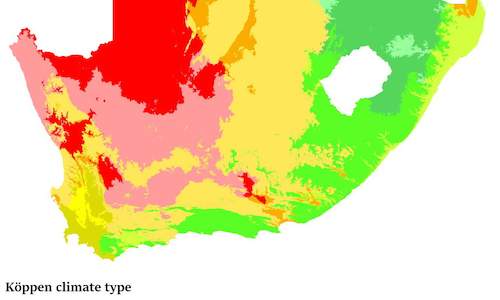
The climate of a farming area determines the suitability of a crop as each crop has specific climatic requirements. South Africa is a hot, d...
more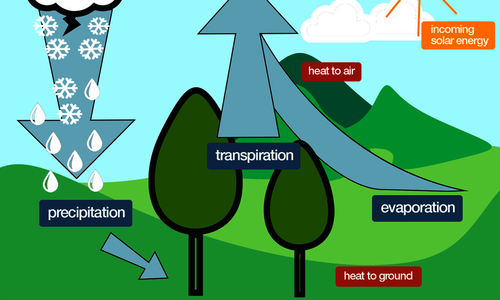
Water can be present in three forms - in solid form as ice, as a liquid, or in the form of gas as water vapour. Evaporation is the process w...
more
Frost is the white layer of frozen water when minimum temperatures at ground level are below 0ºC. Frost can be seen on the ground or on pla...
more
Rain is the precipitation of water drops with diameters greater than 0.5 mm. When the drops are smaller, it is usually called drizzle....
more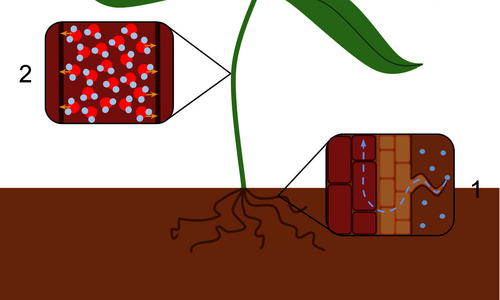
Transpiration is when a plant loses water in the form of water vapour. In the process, water from the plant tissues is lost to the atmospher...
more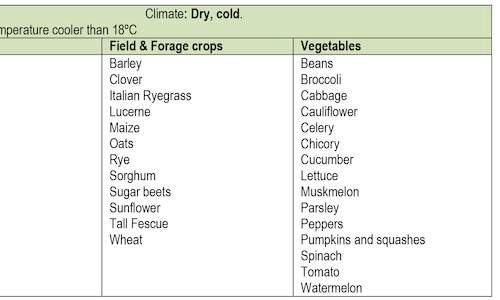
Since irrigated agriculture is expensive and we have a limited water supply in South Africa, it is essential to use water efficiently....
more
 A plant needs periods of heat and cold for certain processes in its growth cycle. These periods of heat and cold are expressed in heat units...
A plant needs periods of heat and cold for certain processes in its growth cycle. These periods of heat and cold are expressed in heat units... In farming areas where frost can damage crops, good management of planting times can limit frost damage during the growth period of crops....
In farming areas where frost can damage crops, good management of planting times can limit frost damage during the growth period of crops.... Similar to rain, hail is a form of precipitation and can contribute to the availability of water in a farming area, but can also cause exten...
Similar to rain, hail is a form of precipitation and can contribute to the availability of water in a farming area, but can also cause exten... Most of South Africa is a summer rainfall area, November to March, while the Western Cape Province receives most of its rain during winter, ...
Most of South Africa is a summer rainfall area, November to March, while the Western Cape Province receives most of its rain during winter, ... Snow, mist and dew are forms of precipitation that contribute to the available moisture in a farming area. Mist is common along the cool are...
Snow, mist and dew are forms of precipitation that contribute to the available moisture in a farming area. Mist is common along the cool are... South Africa falls in a temperate zone, south of the equator, with summers from November to March and winters from May to August. Its temper...
South Africa falls in a temperate zone, south of the equator, with summers from November to March and winters from May to August. Its temper... The climate of a farming area determines the suitability of a crop as each crop has specific climatic requirements. South Africa is a hot, d...
The climate of a farming area determines the suitability of a crop as each crop has specific climatic requirements. South Africa is a hot, d... Water can be present in three forms - in solid form as ice, as a liquid, or in the form of gas as water vapour. Evaporation is the process w...
Water can be present in three forms - in solid form as ice, as a liquid, or in the form of gas as water vapour. Evaporation is the process w... Frost is the white layer of frozen water when minimum temperatures at ground level are below 0ºC. Frost can be seen on the ground or on pla...
Frost is the white layer of frozen water when minimum temperatures at ground level are below 0ºC. Frost can be seen on the ground or on pla... Rain is the precipitation of water drops with diameters greater than 0.5 mm. When the drops are smaller, it is usually called drizzle....
Rain is the precipitation of water drops with diameters greater than 0.5 mm. When the drops are smaller, it is usually called drizzle.... Transpiration is when a plant loses water in the form of water vapour. In the process, water from the plant tissues is lost to the atmospher...
Transpiration is when a plant loses water in the form of water vapour. In the process, water from the plant tissues is lost to the atmospher... Since irrigated agriculture is expensive and we have a limited water supply in South Africa, it is essential to use water efficiently....
Since irrigated agriculture is expensive and we have a limited water supply in South Africa, it is essential to use water efficiently....