
Wine Grape Growing in South Africa
A wine farm near Slanghoek in the Rawsonville district near Worcester in the Western Cape.
The first grapevine was planted in 1659, just after the Dutch landed in the Cape to establish a fresh produce station on the southern tip of Africa. Since then, South Africa's grape industry has grown to more than 10 000 producers, more than half of whom produce wine grapes.
South Africa has become a major player in the world's wine industry and produces a range of wines, from light table wines and full-bodied red wines to Methode Champenoise and Port-wine style wines.
South Africa Online ® presents a range of easy-to-read articles on viticulture in South Africa, inspired by South African research and training material. This is translated in all 11 South African languages, enabling more new farmers and workers to understand and participate in the art of wine grape growing in South Africa.

Viral diseases can be found in any wine-growing region and the occurrence depends on the virus status of the plant material. Plant material ...
more
Canopy management is the process where the vine shoots and leaves are managed in such a way that a good production of the right quality for ...
more
When selecting a specific Cultivar, it should be remembered that the Cultivar may also have one or more clones. Some clones ripen earlier or...
more
Cover Crops are planted between vineyards, often in a rotation system from one year to another. The choice of Cover Crops is mainly determin...
more
The expected lifespan of a vineyard is over twenty years so it is important to ask the right experts for advice. You should look at the suit...
more
The fertility of a vineyard is determined by the budburst. Favourable conditions include enough nutrients, direct sunlight, temperatures abo...
more
A fungus is a microscopically small plant-like organism. Fungal spores are blown or splashed onto the wet vine leaf, cane or grape bunch and...
more
Dead arm disease is caused by the Phomopsis viticola fungus. Botrytis begins as a light brown discoloration of the grape skin....
more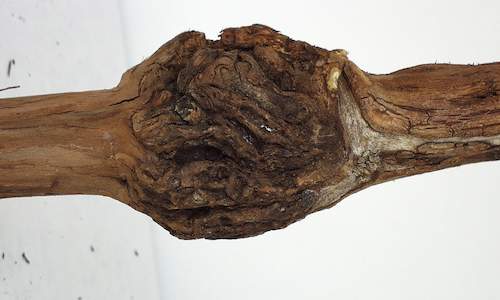
Eutypa dieback is caused by the Eutypa lata fungus. The result is wood decay with the consequent death of the vines. Black Goo is one of sev...
more
Powdery mildew also called oidium, is caused by the fungus Uncinula necator and is considered to be the most serious grapevine fungal diseas...
more
The control of diseases and pests is one of the biggest expenses in wine farming and control measures require the producer to use only certa...
more
The most damaging pests of wine grapes are grapevine mealy bugs, snout beetles and ants. These pests also have a close relationship with eac...
more
These two pests are discussed together, since ants and grapevine mealybugs are usually related and may indicate the presence of the other. G...
more
The margarode is a scale insect that attacks the roots of the vines, usually 40 to 60 cm deep. The first symptom of a margarode infection is...
more
The three types of mites that occur in vineyards are the bud mite, leaf curl mite and erinose mite, of which the bud mite causes the greates...
more
Different snails are found in the Western Cape, for example, the brown garden snail, white dune snail and the banded conical snail. Long-hor...
more
The most common snout beetle in wine grapes is the Phlyctinus callosus. The insect attacks the buds, leaves, vine shoots and grape bunches a...
more
The purpose of grapevine training is to ensure the vines’ cordon arms are equally long and thick and evenly positioned on the cordon wire....
more
A study has found that minimum tillage results in a larger development of soil microbes in the undisturbed sub-layers of the soil than in a ...
more
Mulching is the process of covering the ground surface or berm (soil strip directly below the vine row) with any dead plant material such as...
more
Grapevines are usually planted by the end of winter during July and August. The vines should be planted with the graft union about 5 cm abov...
more
The main purpose of pruning is to get and maintain the desired vine shape for the vineyard for as long as possible. In this way, the trellis...
more
Spray operators have to undergo a medical examination annually. During the management of diseases and pests it should always be remembered t...
more
Soil preparation is the cultivation of the soil before the vineyard is established. One of the most important objectives of soil preparation...
more
Soil types in South Africa differ greatly. Some are very sandy, others have more clay and then there is rocky soil. Soil differs not only in...
more
Before harvesting it is important to set up a harvesting plan. This harvesting plan will include the expected harvest (in tonnes), estimated...
more
Tillage is the mechanical agitation of the soil in a vineyard and is usually associated with the loosening and overturning of the soil. It e...
more
The benefits of trellising include better light intensity in the vines and improved bud fertility. Various trellis systems are currently bei...
more
In dryland vineyards there will be mostly winter and spring-growing weeds and in irrigated areas it is mainly grasses and reeds....
more
After 12 months of caring for the vineyard, it becomes time to harvest. This usually happens from the beginning or mid-January, depending on...
more
To determine the ripeness of wine grapes, both the individual grape berries as well as bunches are tested to determine indicators of ripenes...
more
Compost is decomposed organic material that is applied to serve as nutrients for the soil microbes but not the plant. The effect of compost ...
more
 Viral diseases can be found in any wine-growing region and the occurrence depends on the virus status of the plant material. Plant material ...
Viral diseases can be found in any wine-growing region and the occurrence depends on the virus status of the plant material. Plant material ... Canopy management is the process where the vine shoots and leaves are managed in such a way that a good production of the right quality for ...
Canopy management is the process where the vine shoots and leaves are managed in such a way that a good production of the right quality for ... When selecting a specific Cultivar, it should be remembered that the Cultivar may also have one or more clones. Some clones ripen earlier or...
When selecting a specific Cultivar, it should be remembered that the Cultivar may also have one or more clones. Some clones ripen earlier or... Cover Crops are planted between vineyards, often in a rotation system from one year to another. The choice of Cover Crops is mainly determin...
Cover Crops are planted between vineyards, often in a rotation system from one year to another. The choice of Cover Crops is mainly determin... The expected lifespan of a vineyard is over twenty years so it is important to ask the right experts for advice. You should look at the suit...
The expected lifespan of a vineyard is over twenty years so it is important to ask the right experts for advice. You should look at the suit... The fertility of a vineyard is determined by the budburst. Favourable conditions include enough nutrients, direct sunlight, temperatures abo...
The fertility of a vineyard is determined by the budburst. Favourable conditions include enough nutrients, direct sunlight, temperatures abo... A fungus is a microscopically small plant-like organism. Fungal spores are blown or splashed onto the wet vine leaf, cane or grape bunch and...
A fungus is a microscopically small plant-like organism. Fungal spores are blown or splashed onto the wet vine leaf, cane or grape bunch and... Dead arm disease is caused by the Phomopsis viticola fungus. Botrytis begins as a light brown discoloration of the grape skin....
Dead arm disease is caused by the Phomopsis viticola fungus. Botrytis begins as a light brown discoloration of the grape skin.... Eutypa dieback is caused by the Eutypa lata fungus. The result is wood decay with the consequent death of the vines. Black Goo is one of sev...
Eutypa dieback is caused by the Eutypa lata fungus. The result is wood decay with the consequent death of the vines. Black Goo is one of sev... Powdery mildew also called oidium, is caused by the fungus Uncinula necator and is considered to be the most serious grapevine fungal diseas...
Powdery mildew also called oidium, is caused by the fungus Uncinula necator and is considered to be the most serious grapevine fungal diseas... The control of diseases and pests is one of the biggest expenses in wine farming and control measures require the producer to use only certa...
The control of diseases and pests is one of the biggest expenses in wine farming and control measures require the producer to use only certa... The most damaging pests of wine grapes are grapevine mealy bugs, snout beetles and ants. These pests also have a close relationship with eac...
The most damaging pests of wine grapes are grapevine mealy bugs, snout beetles and ants. These pests also have a close relationship with eac... These two pests are discussed together, since ants and grapevine mealybugs are usually related and may indicate the presence of the other. G...
These two pests are discussed together, since ants and grapevine mealybugs are usually related and may indicate the presence of the other. G... The margarode is a scale insect that attacks the roots of the vines, usually 40 to 60 cm deep. The first symptom of a margarode infection is...
The margarode is a scale insect that attacks the roots of the vines, usually 40 to 60 cm deep. The first symptom of a margarode infection is... The three types of mites that occur in vineyards are the bud mite, leaf curl mite and erinose mite, of which the bud mite causes the greates...
The three types of mites that occur in vineyards are the bud mite, leaf curl mite and erinose mite, of which the bud mite causes the greates... Different snails are found in the Western Cape, for example, the brown garden snail, white dune snail and the banded conical snail. Long-hor...
Different snails are found in the Western Cape, for example, the brown garden snail, white dune snail and the banded conical snail. Long-hor... The most common snout beetle in wine grapes is the Phlyctinus callosus. The insect attacks the buds, leaves, vine shoots and grape bunches a...
The most common snout beetle in wine grapes is the Phlyctinus callosus. The insect attacks the buds, leaves, vine shoots and grape bunches a... The purpose of grapevine training is to ensure the vines’ cordon arms are equally long and thick and evenly positioned on the cordon wire....
The purpose of grapevine training is to ensure the vines’ cordon arms are equally long and thick and evenly positioned on the cordon wire.... A study has found that minimum tillage results in a larger development of soil microbes in the undisturbed sub-layers of the soil than in a ...
A study has found that minimum tillage results in a larger development of soil microbes in the undisturbed sub-layers of the soil than in a ... Mulching is the process of covering the ground surface or berm (soil strip directly below the vine row) with any dead plant material such as...
Mulching is the process of covering the ground surface or berm (soil strip directly below the vine row) with any dead plant material such as... Grapevines are usually planted by the end of winter during July and August. The vines should be planted with the graft union about 5 cm abov...
Grapevines are usually planted by the end of winter during July and August. The vines should be planted with the graft union about 5 cm abov... The main purpose of pruning is to get and maintain the desired vine shape for the vineyard for as long as possible. In this way, the trellis...
The main purpose of pruning is to get and maintain the desired vine shape for the vineyard for as long as possible. In this way, the trellis... Spray operators have to undergo a medical examination annually. During the management of diseases and pests it should always be remembered t...
Spray operators have to undergo a medical examination annually. During the management of diseases and pests it should always be remembered t... Soil preparation is the cultivation of the soil before the vineyard is established. One of the most important objectives of soil preparation...
Soil preparation is the cultivation of the soil before the vineyard is established. One of the most important objectives of soil preparation... Soil types in South Africa differ greatly. Some are very sandy, others have more clay and then there is rocky soil. Soil differs not only in...
Soil types in South Africa differ greatly. Some are very sandy, others have more clay and then there is rocky soil. Soil differs not only in... Before harvesting it is important to set up a harvesting plan. This harvesting plan will include the expected harvest (in tonnes), estimated...
Before harvesting it is important to set up a harvesting plan. This harvesting plan will include the expected harvest (in tonnes), estimated... Tillage is the mechanical agitation of the soil in a vineyard and is usually associated with the loosening and overturning of the soil. It e...
Tillage is the mechanical agitation of the soil in a vineyard and is usually associated with the loosening and overturning of the soil. It e... The benefits of trellising include better light intensity in the vines and improved bud fertility. Various trellis systems are currently bei...
The benefits of trellising include better light intensity in the vines and improved bud fertility. Various trellis systems are currently bei... In dryland vineyards there will be mostly winter and spring-growing weeds and in irrigated areas it is mainly grasses and reeds....
In dryland vineyards there will be mostly winter and spring-growing weeds and in irrigated areas it is mainly grasses and reeds.... After 12 months of caring for the vineyard, it becomes time to harvest. This usually happens from the beginning or mid-January, depending on...
After 12 months of caring for the vineyard, it becomes time to harvest. This usually happens from the beginning or mid-January, depending on... To determine the ripeness of wine grapes, both the individual grape berries as well as bunches are tested to determine indicators of ripenes...
To determine the ripeness of wine grapes, both the individual grape berries as well as bunches are tested to determine indicators of ripenes... Compost is decomposed organic material that is applied to serve as nutrients for the soil microbes but not the plant. The effect of compost ...
Compost is decomposed organic material that is applied to serve as nutrients for the soil microbes but not the plant. The effect of compost ...